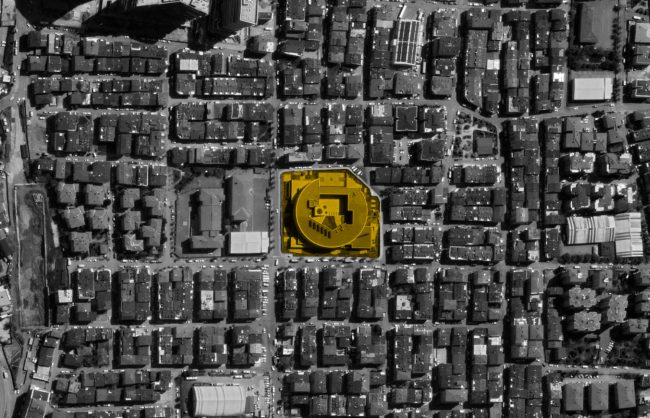
Akşemsettin Primary School is just one of the schools within the scope of the package project “45 Public Buildings in Istanbul“ designed and projected by Uygur. The schools, which were decided to be demolished and rebuilt in Istanbul within the scope of ISMEP (Istanbul's Seismic Risk Mitigation and Emergency Project), are designed in a unique way in their own context, on the same plot by increasing their capacity.
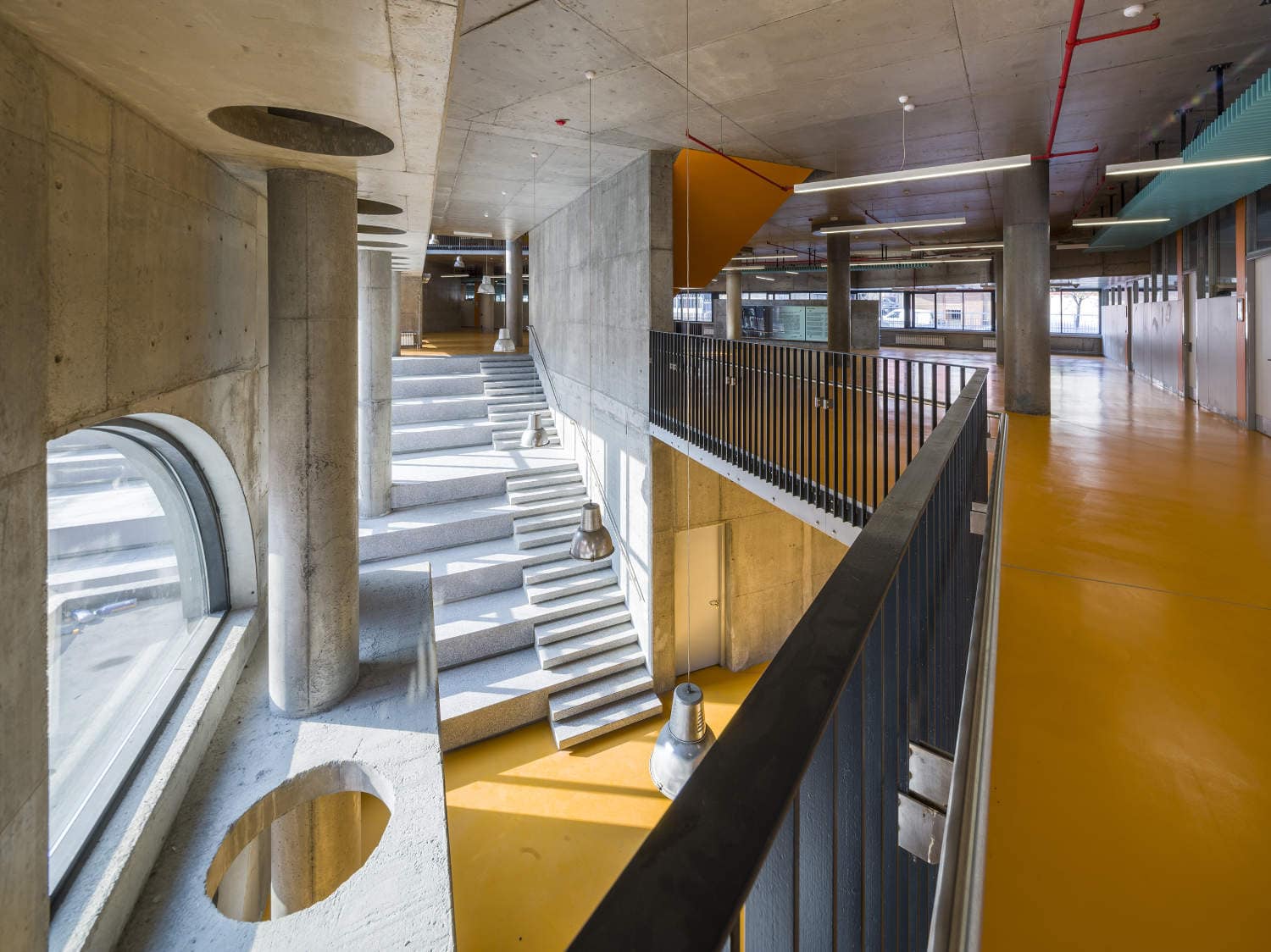

From architects’ standpoint, it is important to reconstitute the architectural and social significance of Akşemsettin Primary School, located in Küçükcekmece, where the dense slum areas are now transforming into mass housing projects, and the population is still increasing. Considering the rapidly developing, unplanned and evasive construction in this neighborhood, to design qualified image of a "new" building for an educational institution in a way that is contemporary and befitting the Republic of Turkey, is considered as a significant architectural emphasis.
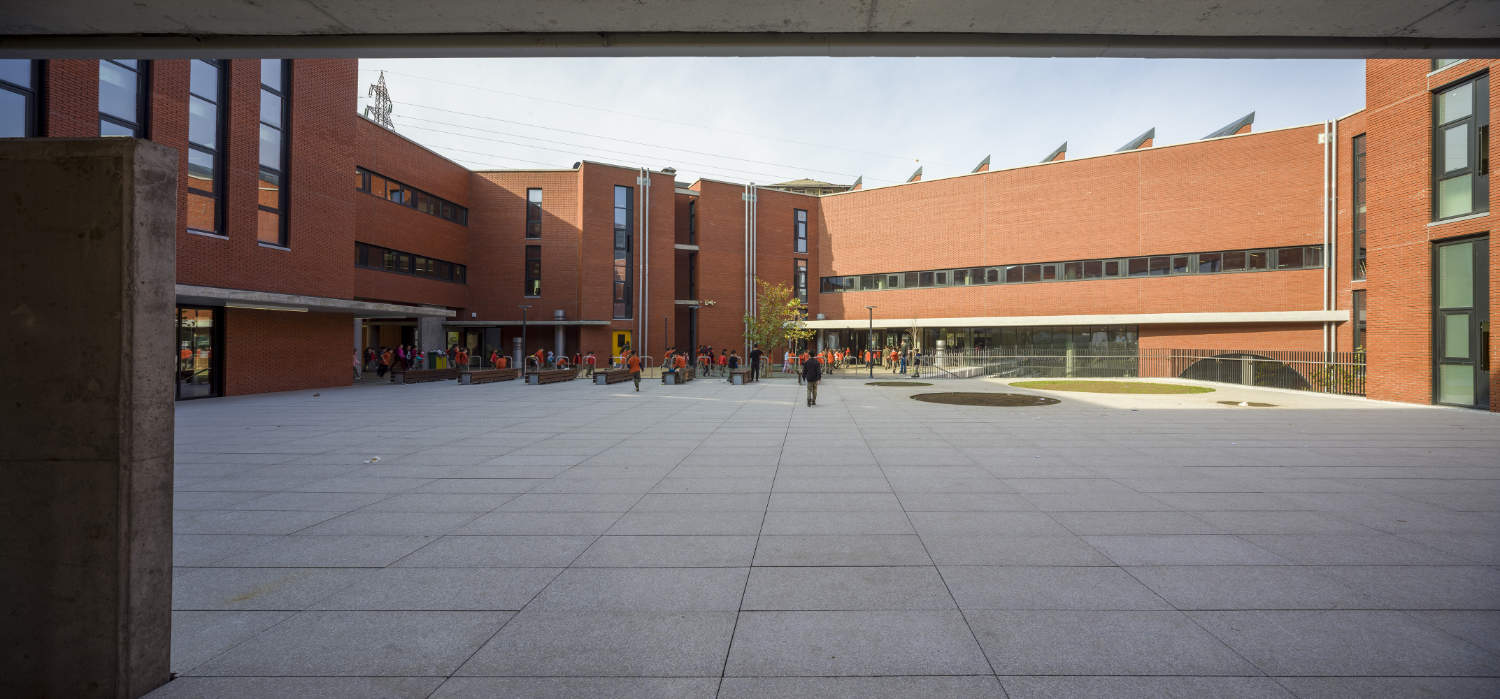
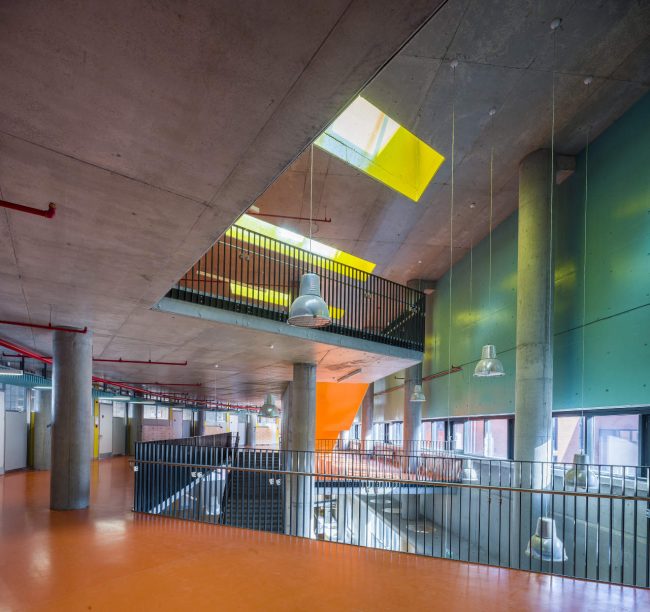
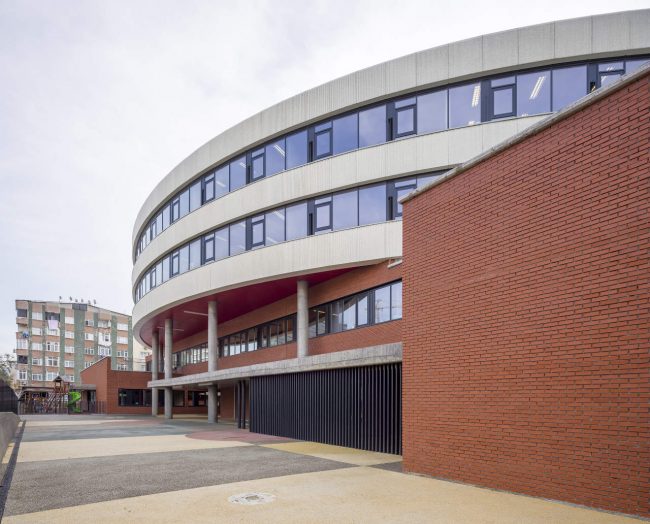
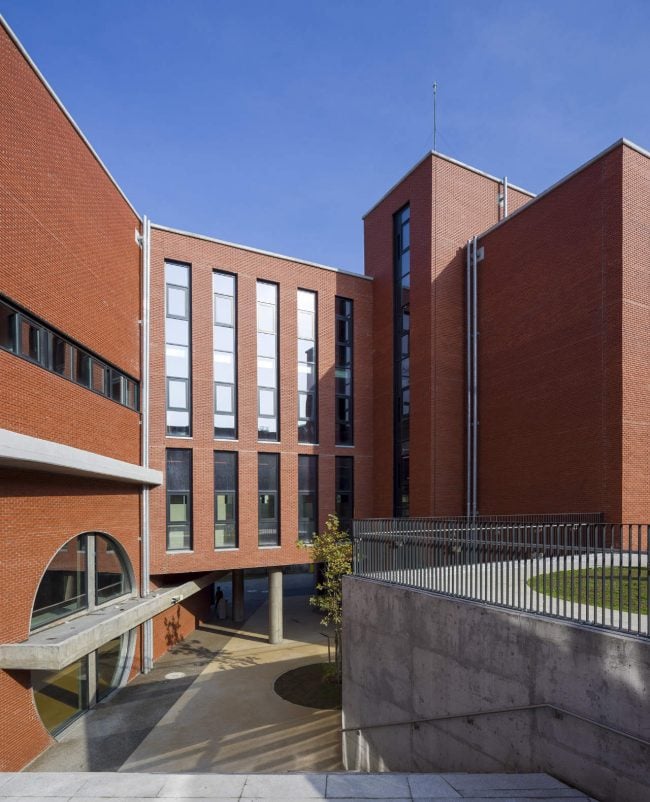
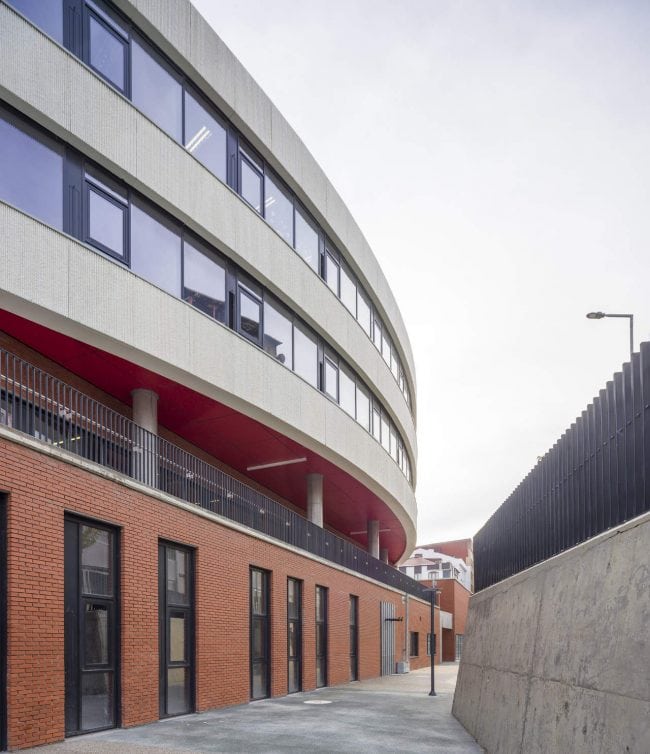
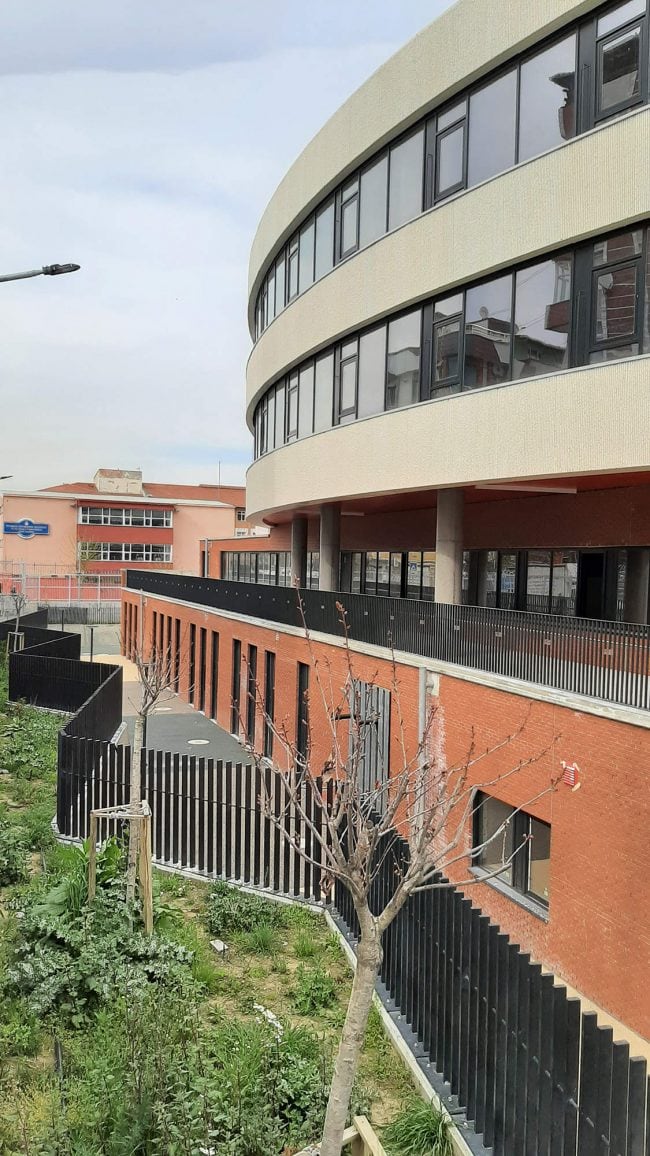
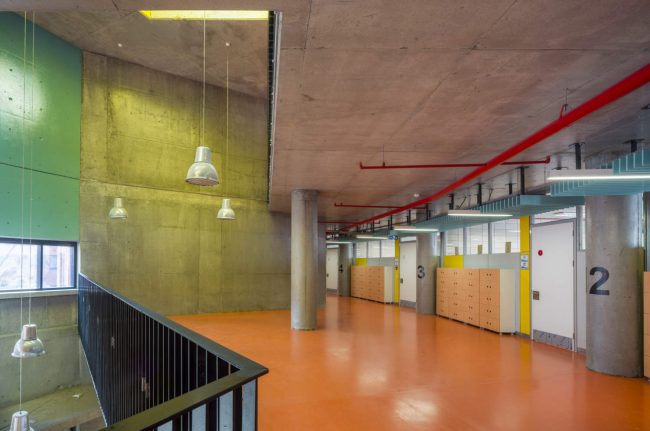
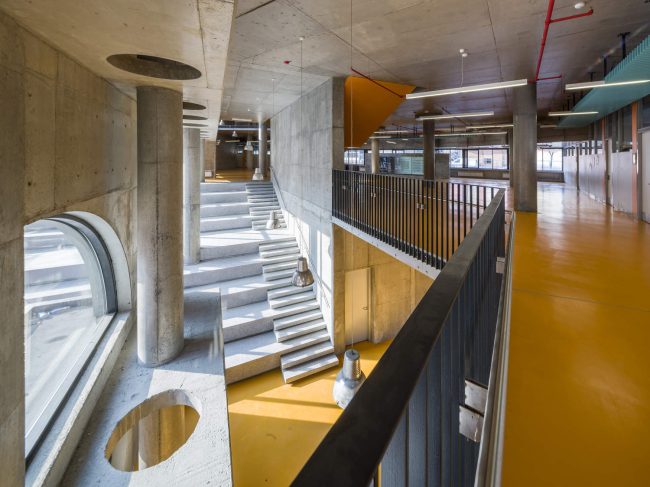
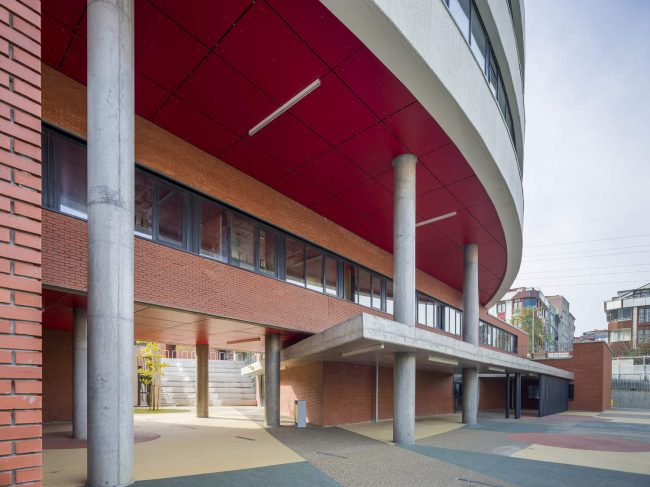
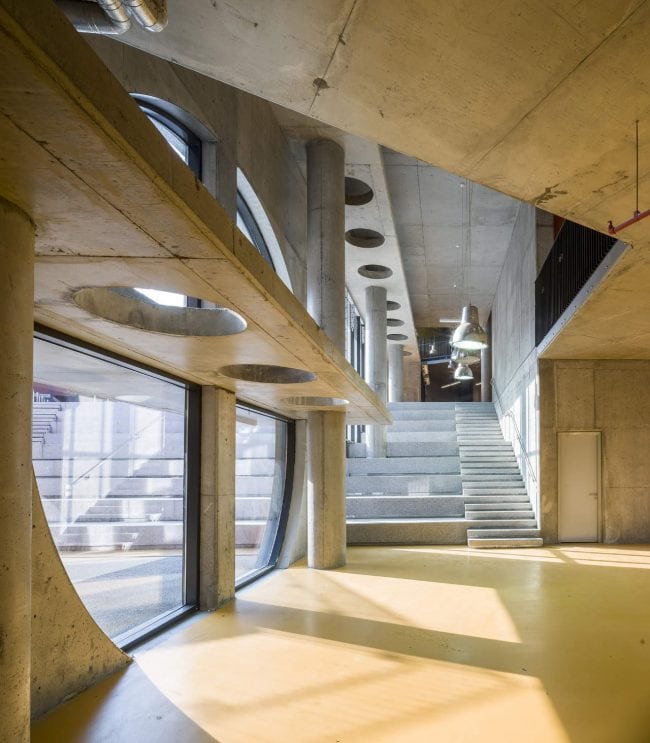
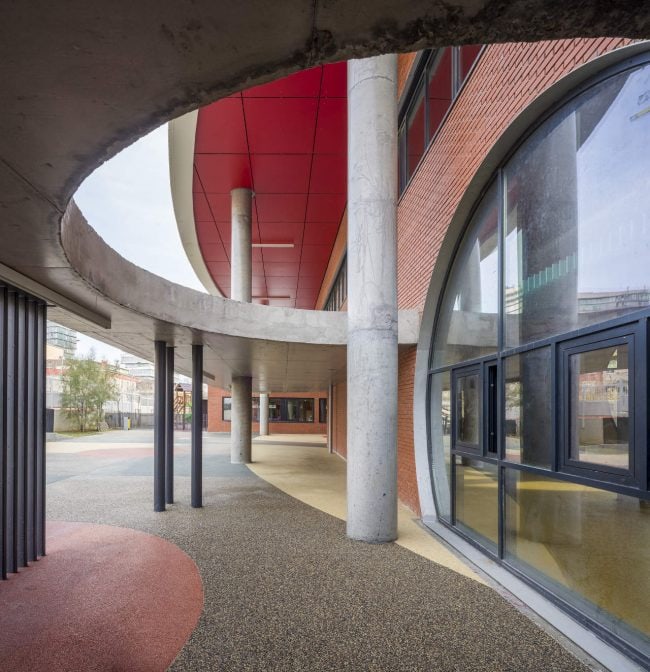
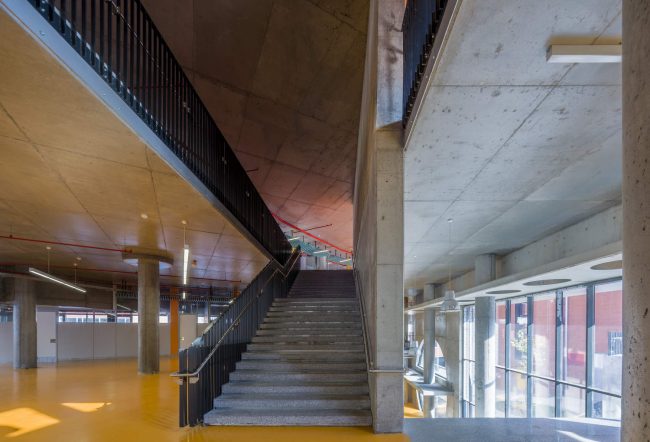
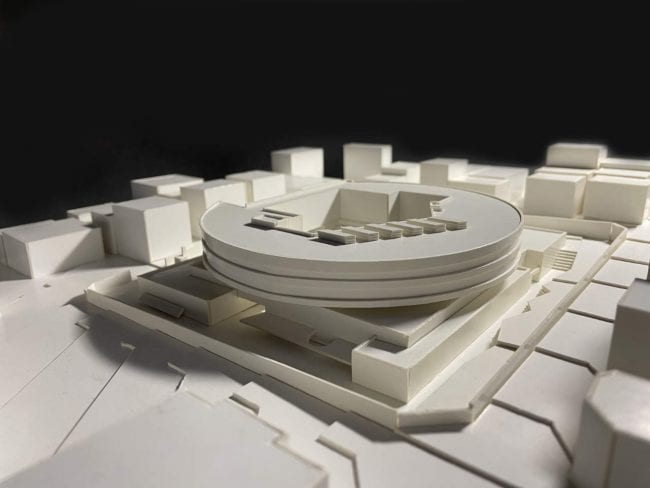
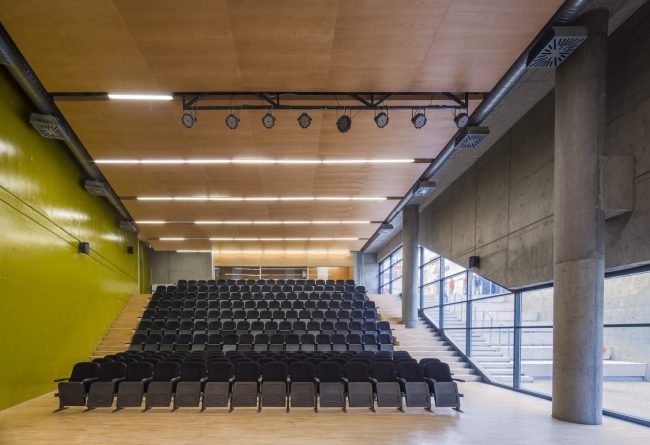
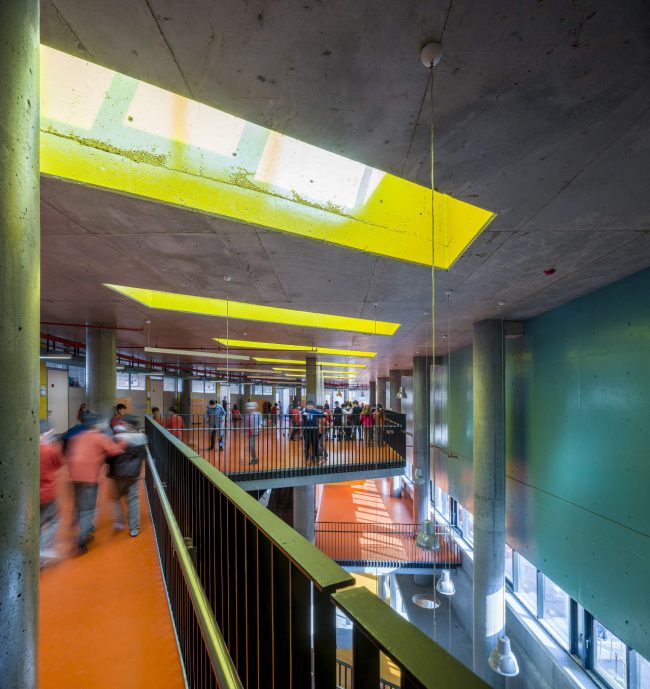
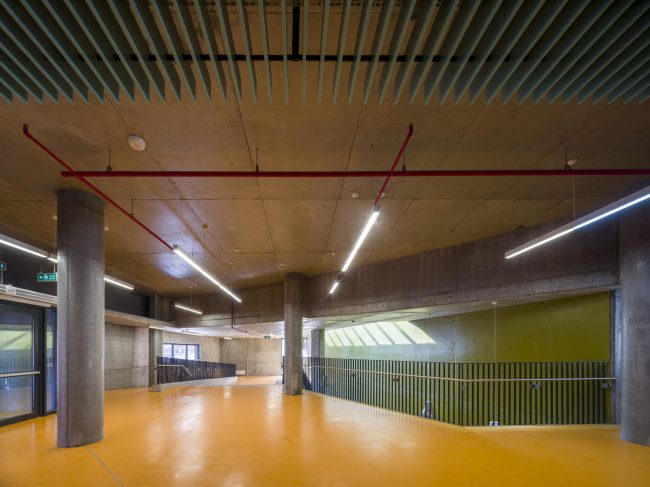
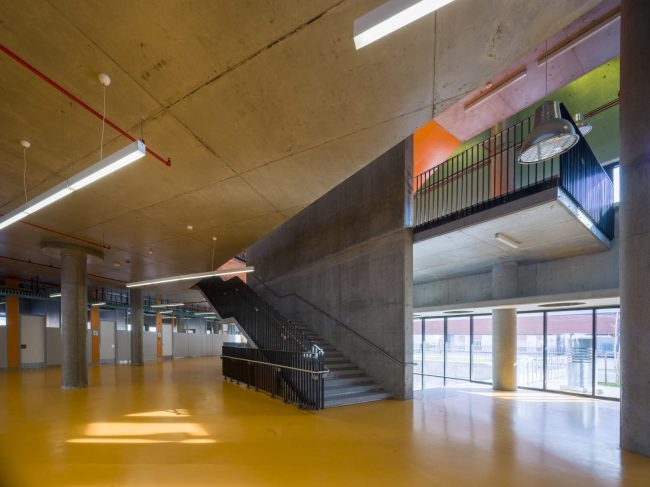
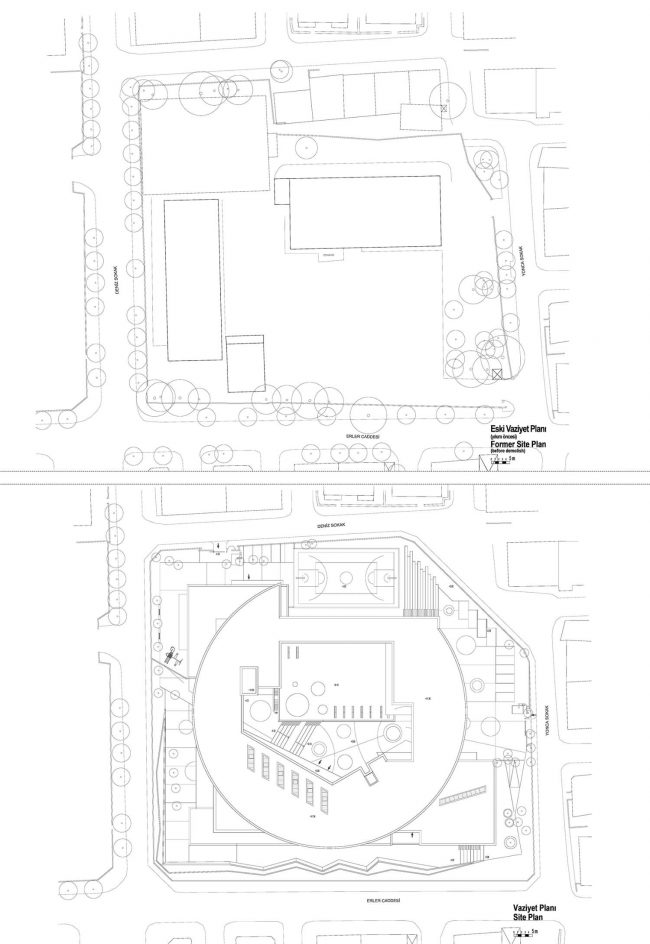
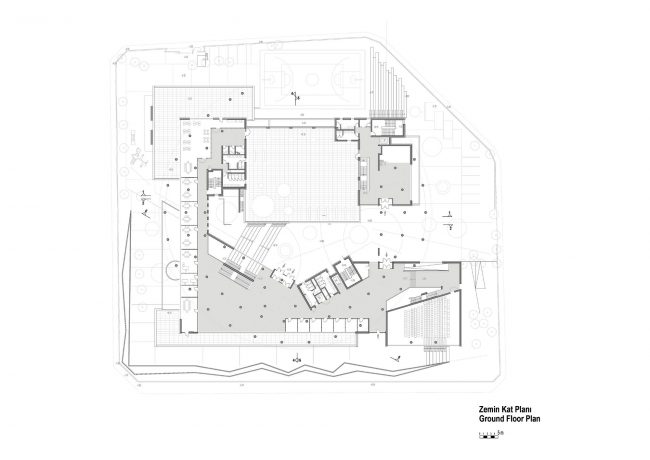
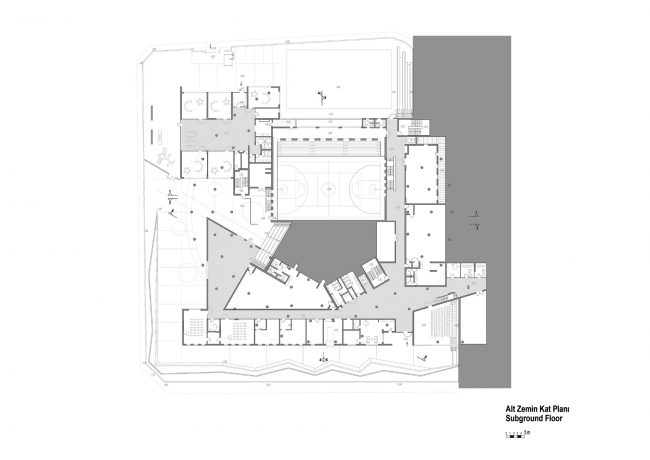
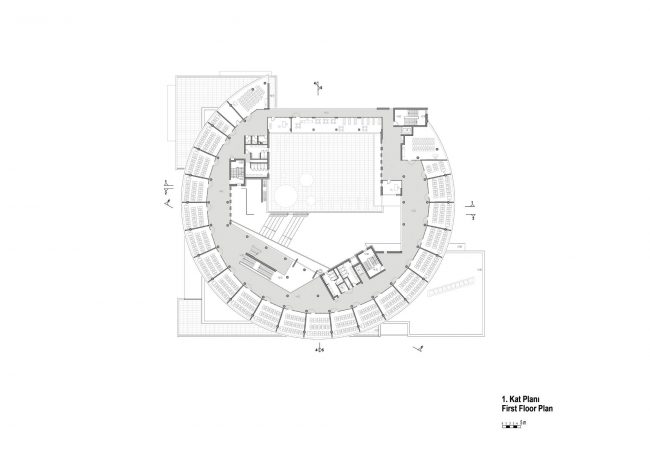
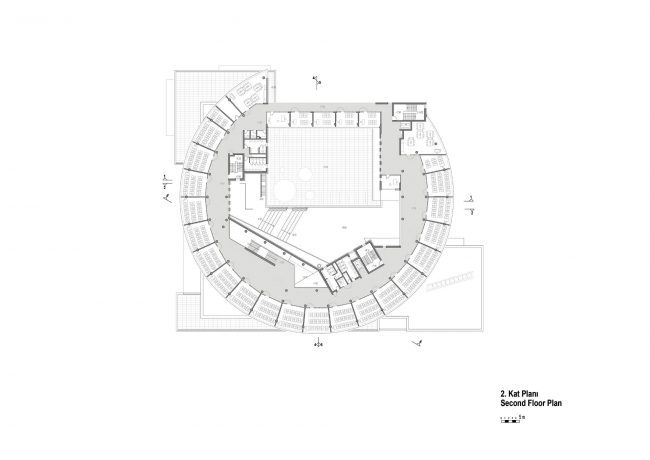
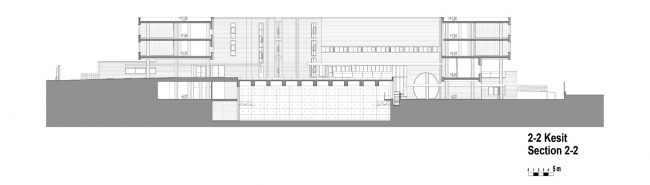
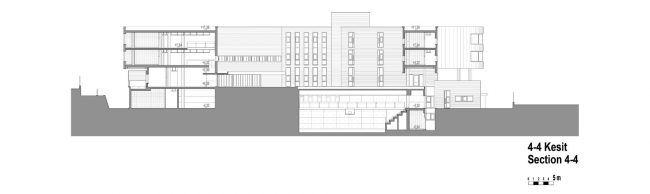
Akşemsettin Primary School was continuing education until 2018 in a building with a high earthquake risk in a congested area of 3.497 m2 with a total of 35 (thirty-five) classrooms and 2 (two) kindergarten rooms with a capacity of 1400 students. Uygur Architects aims to improve and modernize the spatial quality on the new school building. Even though while increasing the school program, the mass-open area ratio numerically changes, it is resolved in a balanced composition and strategic interpretation of mass relations. Several orthogonal units in which the common and social programs are organized, are placed on ground level utilizing the land level differences. The calculated wholeness of these units forms a plinth and a courtyard is defined in the middle. The node of social interaction networks is resolved at the sub-ground floor and ground floor. A compact disc form, in which classroom units and repetitive programs are gathered together, is superposed on top of the plinth. The in-between spaces emerged in this fragmented mass composition, find their own definitions as areas of social interaction overlap.
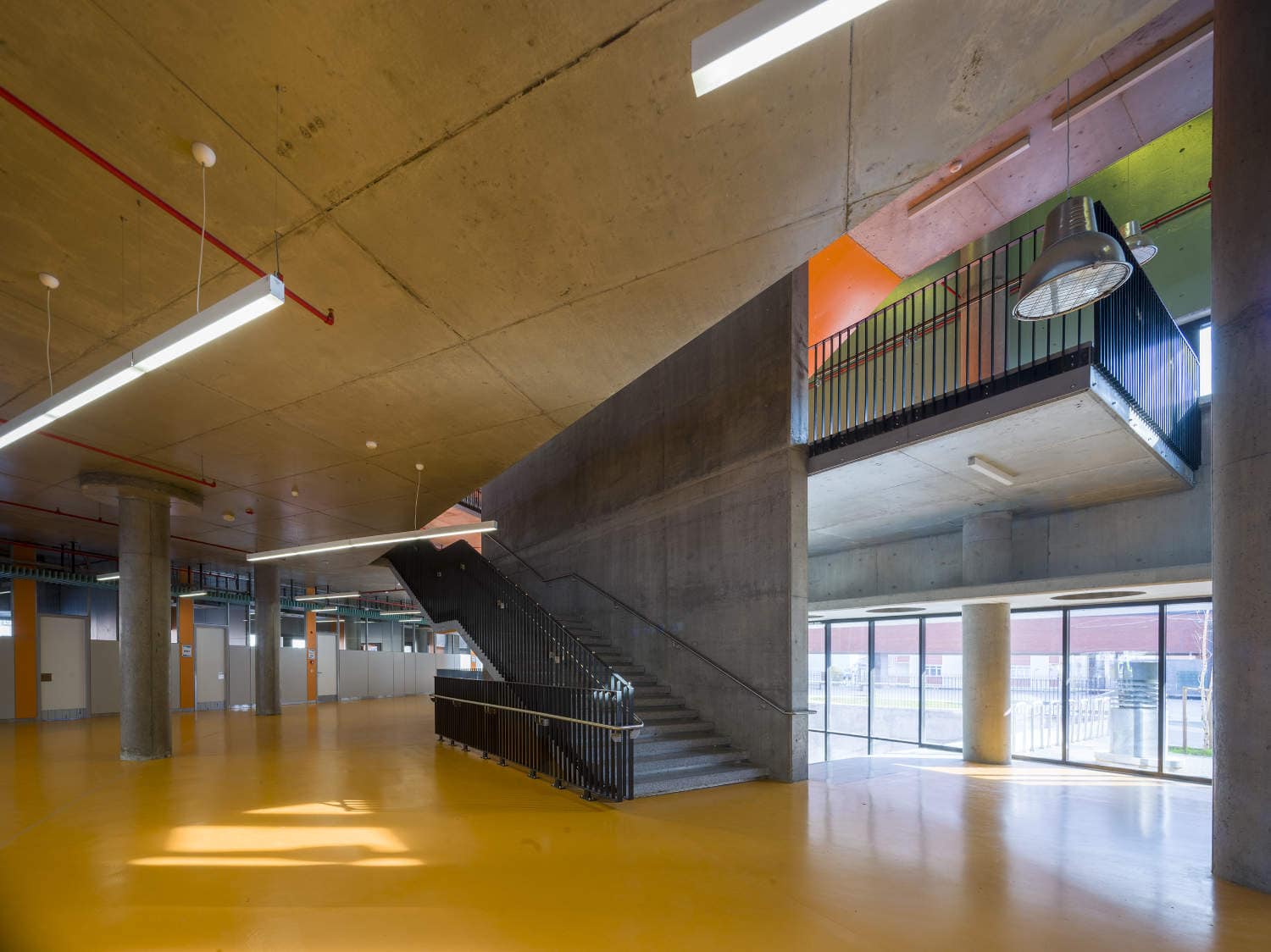

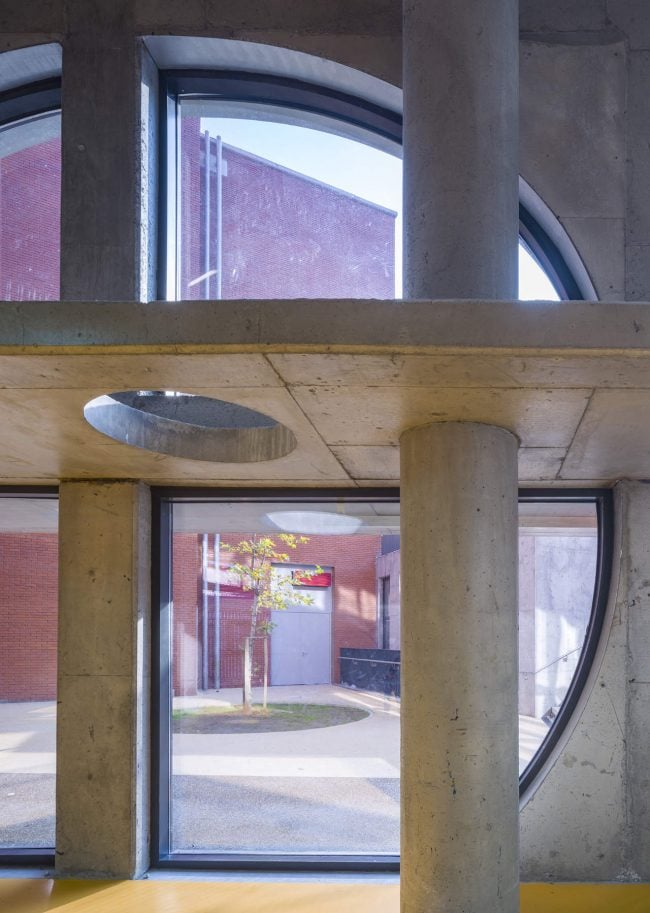
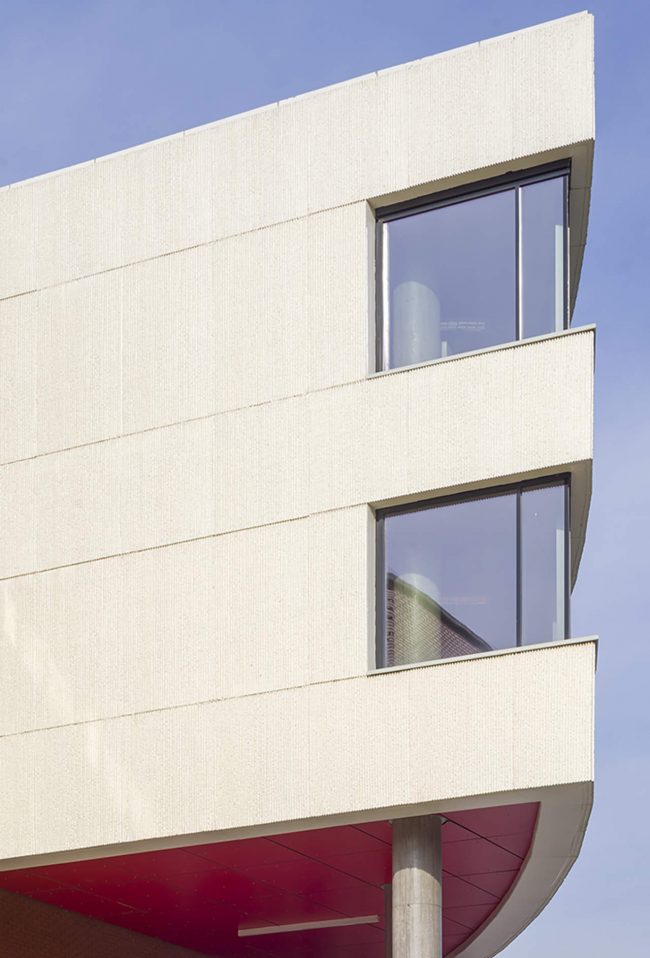
As the schools that were demolished and rebuilt due to earthquake resistance within the scope of ISMEP went to other schools during the construction process, these new schools have to be built both economically and rapidly. As a solution to this, Uygur Architects formulated a strategic method by designing a library of materials and details. While every single project is uniquely designed, architects who interpret this library as an "alphabet" construct different sentences for each plot. In the case of Akşemsettin Primary School, brick and exposed concrete stand out; however, the façade of the disc mass is customized by the textured concrete.
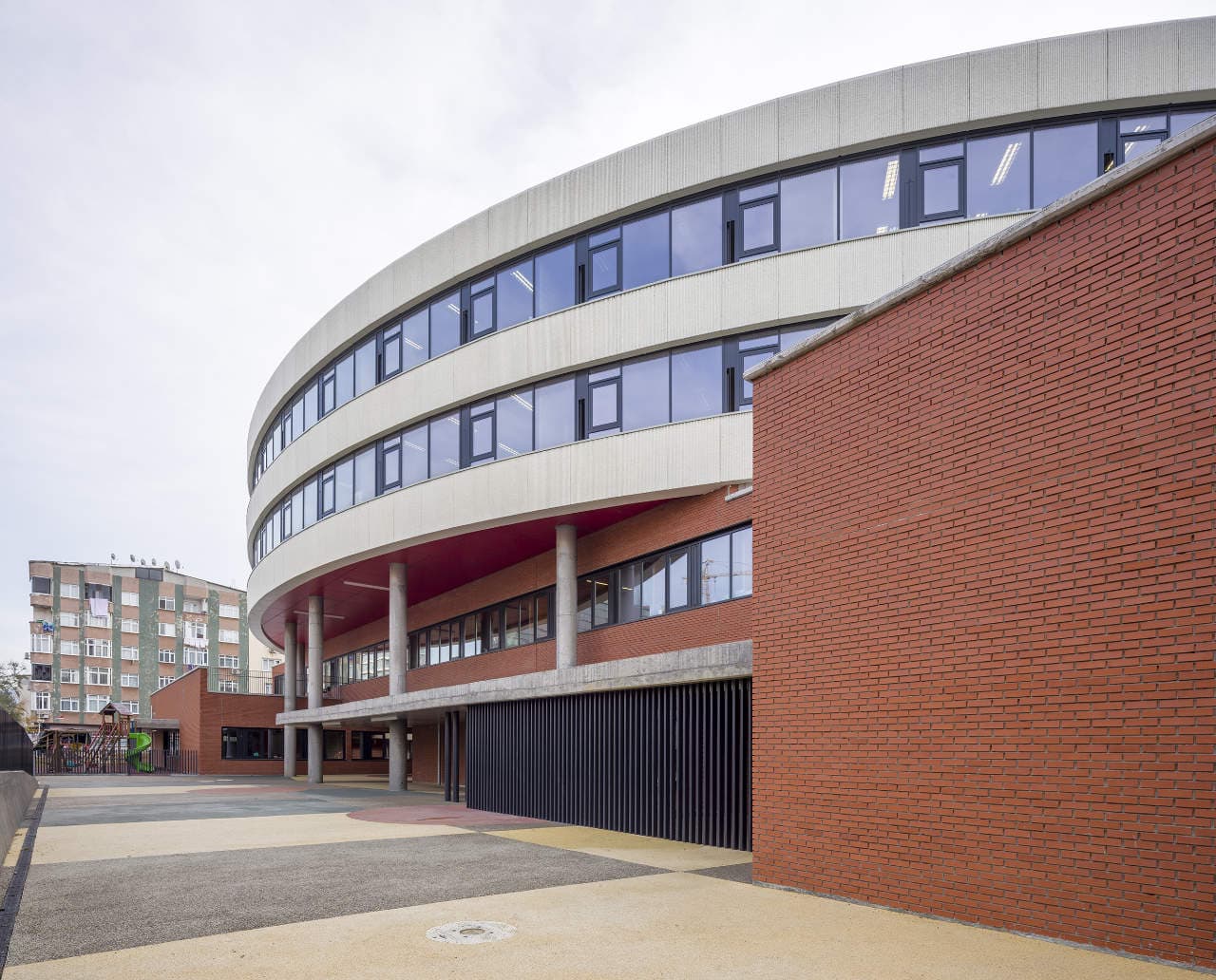

With the additional areas of social areas, common areas, laboratories, sports fields, multi-purpose halls etc. the total construction area of the demolished building increases 2.5 times and becomes 11,669 m2. The number of classes, which was 37 in the demolished school, whose student capacity did not change, increased to 56 with music rooms, support education rooms, laboratories, painting workshops and kindergarten game rooms that increased from 2 to 5.
45 Public Buildings in Istanbul
The project consists of the rehabilitation of 45 public buildings in various districts of Istanbul, Turkey within the Istanbul Seismic Master Plan. Except few buildings the project is mainly focuses on schools in İstanbul. The works related to the rehabilitation program includes demolition of the existing buildings, data collection, architectural and engineering design studies, preparation of construction tender documents and provision of supervision services during the construction works. Uygur Architects carried out the architectural design, engineering design coordination, preparation of construction tender documents and provision of architectural supervision during the construction works.
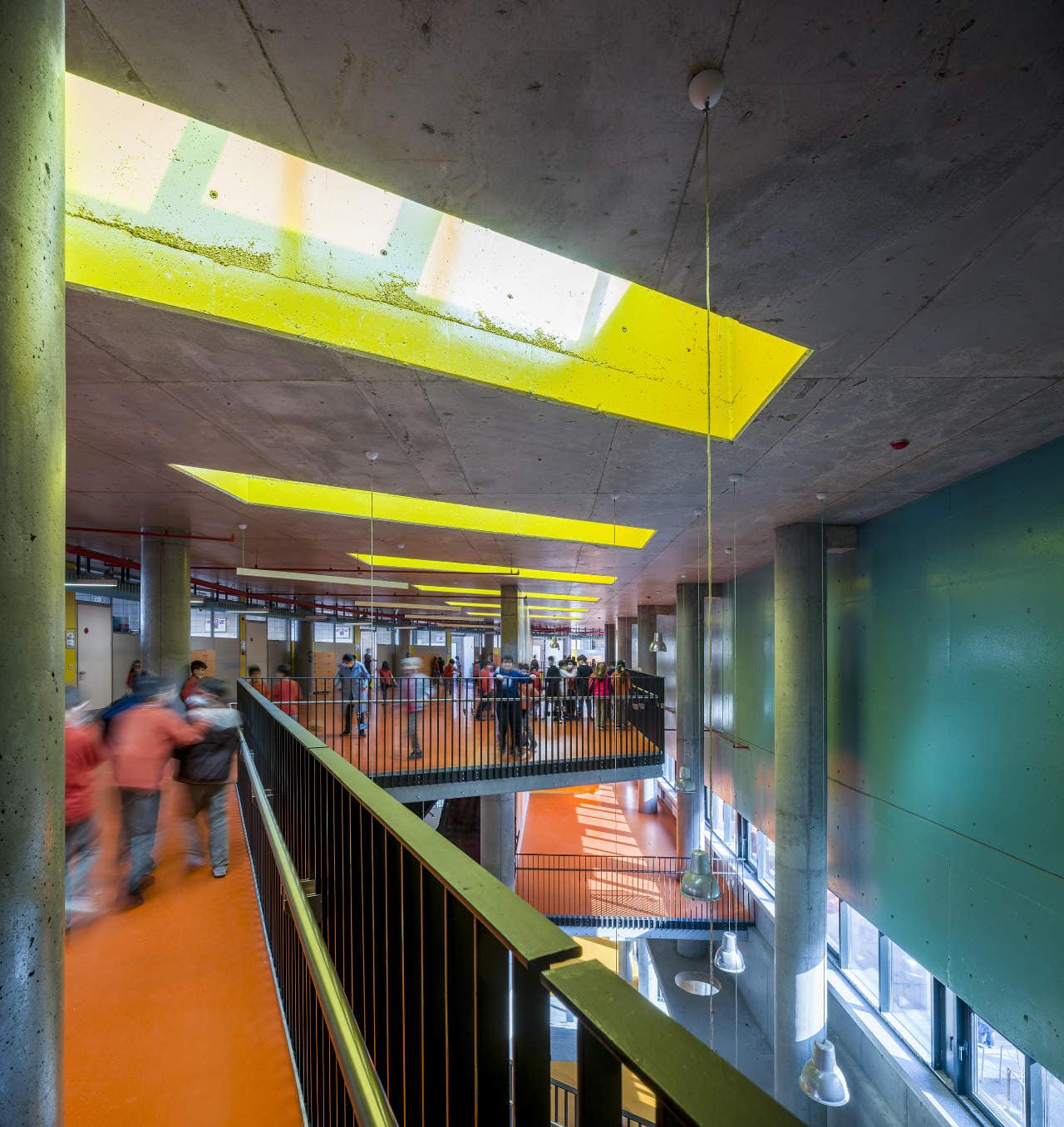

Architects considered this project as an important opportunity for modernization of the educational spaces. According to the architects’ approach, each school should have its own identity instead of applying a typical project, which is the most accepted by the Ministry of Education. Thus, even though the new schools have the same concept, each of them is designed separately within its own context. Besides, as a significant design principle, contemporary education understanding is adopted by composing various indoor and outdoor common spaces. Considering the fact that schools are the first social public spaces children could experience, predominantly the common spaces generate the educational framework of school designs. Each project was designed with the awareness that educational units not only are for students, but also improve the learning desire, environmental conscience and spatial taste of the residents in city life. In order to design socially sustainable and energy-saving buildings, the structural components are designed and constructed without any paint or coating.
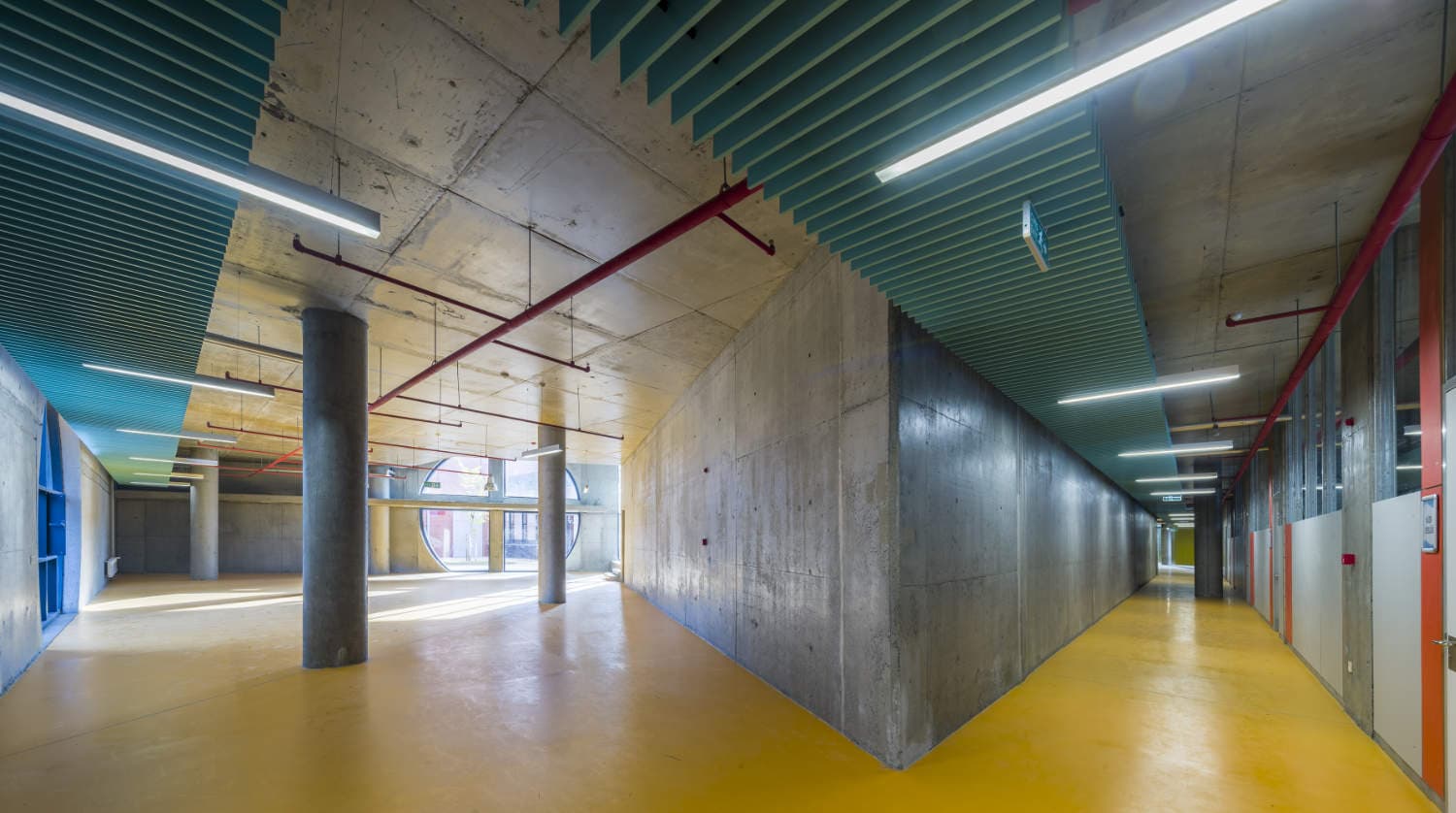

Rehabilitation program of schools includes demolition of existing schools and construction of the new ones. Following the demolition of existing structures, the students would be temporarily transferred to neighboring schools. Therefore, an organized work program was adapted in order to decrease the negative impact of a dense capacity on the neighboring school. Supporting this approach, architects composed a construction methodology and building materials selection in order to diminish the construction period so that the students would be transferred to their original schools at earliest possible. Due to the nature and age of the building’s users, the materials to be used were selected in terms of their durability and ease of maintenance. The main purpose of selecting such materials was to avoid shorter periodic maintenance.